Incident Response and Breach Readiness: Preparing for the Inevitable
Cyber incidents are no longer a matter of “if” but “when.” Even organizations with strong preventive controls can experience breaches due to sophisticated attacks, human error, or third-party exposure.
Incident response and breach readiness focus on minimizing impact, restoring operations quickly, and maintaining trust when security failures occur.
Why Incident Response Matters
Without a structured incident response capability, organizations often react chaotically to security incidents. Delays, miscommunication, and unclear responsibilities increase financial and reputational damage.
Effective response enables organizations to contain threats, preserve evidence, and make informed decisions under pressure.
- Faster containment of active threats.
- Reduced downtime and operational disruption.
- Improved coordination across teams.
- Clear accountability during crises.
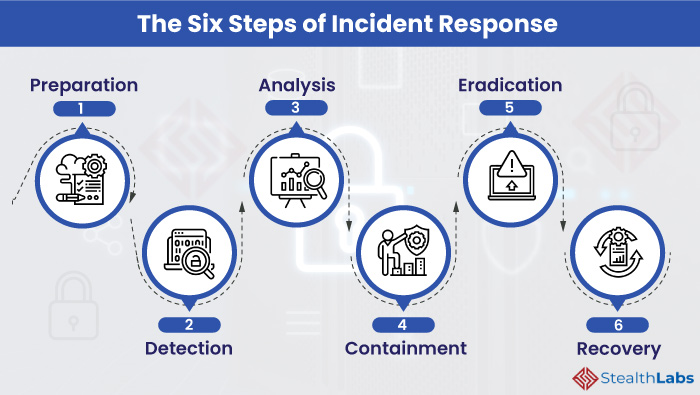
Key Phases of Incident Response
Incident response follows a lifecycle that guides organizations from preparation through recovery. Skipping steps or improvising increases the risk of incomplete remediation.
Each phase plays a critical role in minimizing damage.
- Preparation and readiness planning.
- Detection and analysis of incidents.
- Containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Post-incident review and improvement.
Roles and Responsibilities During a Breach
Incident response is not solely a technical function. Legal, communications, HR, and executive leadership all play essential roles during a breach.
Clearly defined responsibilities prevent confusion and conflicting actions.
- Security teams handle technical investigation.
- Legal teams assess regulatory obligations.
- Communications manage internal and external messaging.
- Leadership provides strategic direction.
Testing and Improving Breach Readiness
Plans that are never tested often fail in real incidents. Tabletop exercises and simulations help teams identify gaps and improve coordination.
Continuous improvement ensures readiness evolves alongside the threat landscape.
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises.
- Simulate ransomware and insider scenarios.
- Review lessons learned after incidents.
- Update response plans based on findings.
Integrating Incident Response with Security Strategy
Incident response should be embedded into broader security governance rather than treated as a standalone activity.
Integration ensures that detection, response, and recovery align with business priorities.
- Align response plans with risk management.
- Integrate logging and monitoring tools.
- Ensure executive visibility and support.
- Coordinate with third-party providers.
Conclusion
Incident response and breach readiness are critical capabilities for modern organizations. Preparation, clarity, and continuous improvement enable faster recovery and reduced impact.
By investing in structured response planning, enterprises can turn inevitable incidents into manageable events rather than business-ending crises.



Leave a Reply