AI and Cybersecurity: Opportunities and Threats
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape at an unprecedented pace. Organizations increasingly rely on AI-driven systems to detect threats, automate responses, and analyze vast amounts of security data. At the same time, threat actors are weaponizing AI to launch more sophisticated, scalable, and evasive cyberattacks.
This dual-use nature of AI presents both significant opportunities and serious risks. Understanding how AI strengthens cybersecurity defenses-and how it can be abused by attackers-is critical for building resilient digital environments.
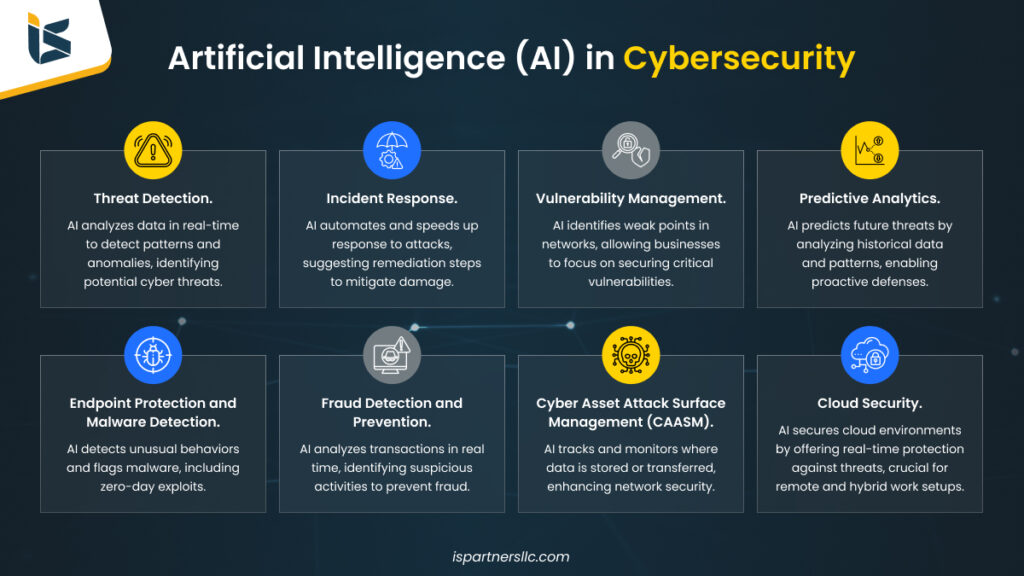
How AI Enhances Cybersecurity Defense
AI enables security teams to move beyond manual analysis and static rule-based systems. Machine learning models can process massive volumes of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that would otherwise go unnoticed.
This capability allows organizations to detect threats faster, reduce false positives, and respond to incidents with greater precision.
- Real-time threat detection through behavioral analysis.
- Automated incident response and containment.
- Improved accuracy by reducing alert fatigue.
- Continuous learning from new attack techniques.
AI in Threat Intelligence and Prediction
AI-powered threat intelligence systems analyze data from multiple sources, including logs, threat feeds, and external intelligence reports. These systems identify emerging attack trends and predict potential threats before they materialize.
Predictive intelligence enables proactive defense strategies, helping organizations prepare for attacks rather than reacting after damage has occurred.
- Correlation of indicators of compromise across environments.
- Prediction of attacker behavior using historical data.
- Faster prioritization of high-risk threats.
- Improved decision-making for security leaders.

AI-Driven Cyber Threats
While defenders benefit from AI, attackers are also leveraging the same technology. AI enables threat actors to automate reconnaissance, generate convincing phishing messages, and evade traditional detection mechanisms.
These AI-driven attacks scale rapidly and adapt dynamically, making them harder to detect using conventional security tools.
- Highly realistic phishing and social engineering campaigns.
- Automated malware mutation to evade detection.
- AI-assisted vulnerability discovery.
- Deepfake-based identity and voice fraud.
Risks and Limitations of AI in Security
Despite its benefits, AI is not a silver bullet. Poor data quality, biased models, and lack of transparency can introduce new risks into security operations.
Overreliance on automated decision-making without human oversight may lead to missed threats or incorrect responses.
- Bias and blind spots in training data.
- Explainability challenges in AI-driven decisions.
- Potential manipulation of AI models by attackers.
- False sense of security due to automation.
Balancing AI Automation with Human Expertise
The most effective cybersecurity strategies combine AI-driven automation with human judgment. AI excels at processing data at scale, while human analysts provide contextual understanding and strategic decision-making.
Organizations should design security operations where AI supports analysts rather than replacing them.
- Use AI to augment, not replace, security teams.
- Maintain human oversight for critical decisions.
- Regularly validate and tune AI models.
- Train staff to understand AI capabilities and limitations.
Conclusion
AI is fundamentally changing cybersecurity, offering powerful tools to detect, predict, and respond to threats. At the same time, it introduces new risks as attackers exploit the same technologies to enhance their capabilities.
Organizations that understand both the opportunities and threats of AI will be best positioned to build resilient security strategies. A balanced approach-combining AI innovation, human expertise, and ethical governance-will define the future of effective cybersecurity defense.



Leave a Reply