Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protecting Sensitive Information in the Modern Enterprise
Data is one of the most valuable assets an organization owns. Customer records, intellectual property, financial information, and proprietary research all represent critical business value. When sensitive data is lost, leaked, or exposed, the consequences can be severe.
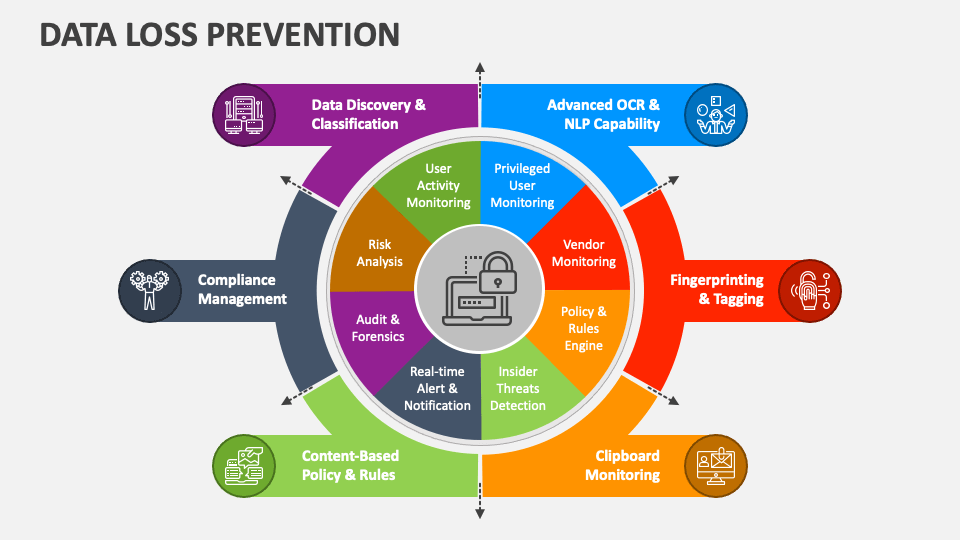
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) focuses on identifying, monitoring, and protecting sensitive information across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. As data moves more freely than ever, DLP plays a vital role in reducing both external and insider-driven risks.

Why Data Loss Is a Growing Risk
Modern enterprises operate in highly distributed environments. Employees access data from remote locations, personal devices, and cloud platforms, increasing the likelihood of accidental or malicious data exposure.
Data loss is no longer limited to cyberattacks. Misconfigurations, human error, and poor access controls contribute significantly to data leakage incidents.
- Remote work expands data access points.
- Cloud storage increases data sharing.
- Insider threats remain difficult to detect.
- Regulatory penalties amplify business impact.
What Is Data Loss Prevention?
DLP is a strategy that combines technology, policies, and processes to ensure sensitive data is not accessed, shared, or transmitted improperly.
Effective DLP programs begin with understanding where sensitive data resides and how it is used across the organization.
- Data discovery and classification.
- Policy enforcement based on data sensitivity.
- Monitoring of data movement.
- Prevention of unauthorized sharing.

Common Causes of Data Leakage
Not all data loss incidents are malicious. Many occur due to simple mistakes or lack of awareness. Without proper controls, employees may unintentionally expose sensitive information.
Understanding common causes helps organizations design practical and effective DLP controls.
- Sending sensitive data to the wrong recipient.
- Uploading confidential files to unsecured cloud services.
- Using personal email or storage for work data.
- Excessive access permissions.
DLP Across Cloud and Endpoints
Traditional network-based DLP is no longer sufficient. Organizations must extend data protection to endpoints, SaaS applications, and cloud infrastructure.
Modern DLP solutions provide visibility and control wherever data travels.
- Endpoint DLP to monitor local data usage.
- Cloud DLP for SaaS and storage platforms.
- Email DLP to prevent accidental sharing.
- Integration with identity and access controls.
Building an Effective DLP Strategy
DLP programs should balance security with usability. Overly restrictive policies can disrupt business operations and encourage risky workarounds.
Successful DLP strategies focus on visibility, education, and gradual enforcement.
- Start with monitoring before blocking.
- Align policies with business workflows.
- Educate employees on data handling.
- Continuously refine policies based on risk.
Conclusion
As data becomes more distributed, protecting it requires more than traditional perimeter defenses. Data Loss Prevention provides organizations with the visibility and control needed to safeguard sensitive information.
By implementing a thoughtful DLP strategy, enterprises can reduce risk, support compliance, and enable secure data-driven operations.


Leave a Reply